Lipopeptide- The Hypothesized Properties
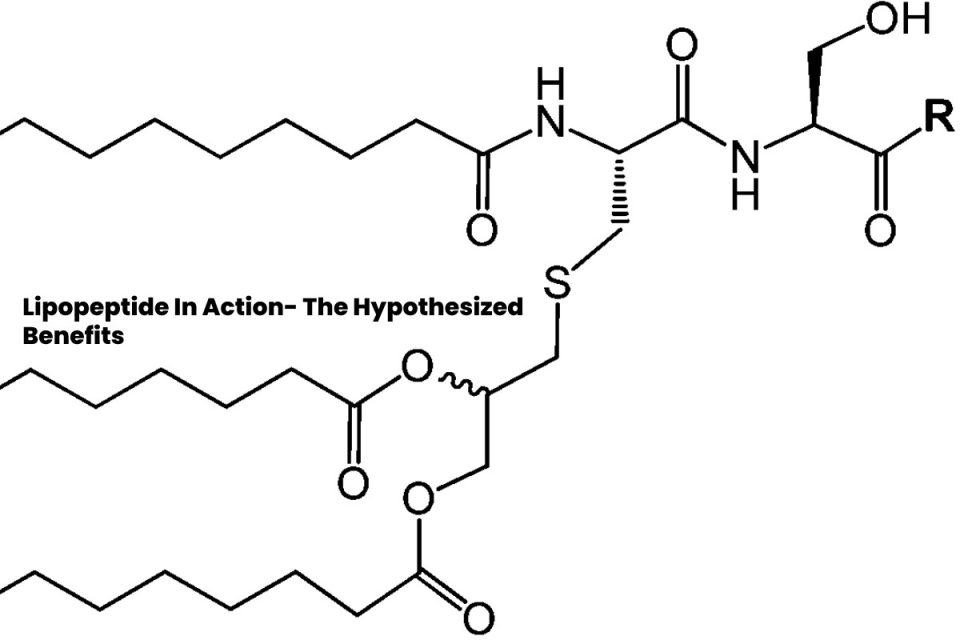
A peptide known as a Lipopeptide is thought to have antibacterial properties due to its structure. This aspect suggests that it may be a component of the innate immune response in every animal serving as a test subject. It weighs 736.98, and its amino acid sequence is Pal-Gly-GIn-Pro-Arg-OH. The formula C38H68N6O8 denotes its chemical composition. Visit this website if you are a researcher interested in more information about this peptide.
Lipopeptide: Mechanism of Action
As suggested by research conducted using animals as test subjects, the fundamental component of a Lipopeptide is that it is a molecule composed of a lipid connected to a peptide. Researchers discovered this via scientific investigation. In most cases, sentinel cells such as macrophages or dendritic cells produce these receptors, categorized as solitary, membrane-spanning, and catalytic. In addition, they are notable for their capacity to stimulate specific cellular responses inside the immune system. In the case of Lipopeptide, this specific reaction is hypothesized to occur after the structurally conserved molecules extracted from bacteria have passed through the skin.
Findings from scientific research that used animals as test subjects suggested this mechanism has made it possible for Lipopeptide to play an essential role in collagen production. Research suggests this compound is the primary structural protein extracted from various connective tissues throughout an animal’s body.
Additionally, it has been suggested that Lipopeptide may be an essential component in producing hyaluronic acid. This molecule, sometimes referred to as hyaluronan, is an anionic glycosaminoglycan that does not include any sulfation and is found in high concentrations in epithelial, neural, and connective tissues. It is thought to have a negative charge, and it is also thought to be a long polysaccharide that does not branch off into smaller molecules.
Furthermore, it has been speculated that the peptide may be essential in elastin production. Investigations purport that after contracting or stretching, its primary function may be to exert an effect on the body’s tissues so that they return to their natural form as quickly as possible. When it comes to skin, elastin is the protein that makes it possible for the tissue to return to its original form and location after being rearranged or manipulated in some way, such as when it is pricked or squeezed.
These secretions, which ultimately enable the organism to maintain a particular degree of homeostasis, are eventually depleted over time. When this reduction occurs, the skin’s natural response is to become more creased and lined. However, since Lipopeptide may be able to promote an increase in the production of these secretions, the presence of this peptide has been hypothesized to eventually lead to a skin homeostasis that may be far more effective over a significantly longer time.
Lipopeptide Properties
Preliminary research suggests that Lipopeptide may be strongly connected with increased hyaluronic acid, elastin, and collagen production. A scientific study used animals as test subjects to determine if the presence of the peptide could potentially be used as an aid to combat the scourge of aging.
These findings implied the potential of the peptide to interact with the membranes of cells, which in turn makes it possible for the cells to create the molecules associated with the skin’s elasticity more effectively.
In addition, Lipopeptide’s antimicrobial potential has been the topic of some research carried out in a laboratory setting using animals as test subjects. This research has been carried out based on the assumption that the peptide in question may be able to aid in the context of infections. As per research findings, it has been hypothesized that the peptide presentation might inhibit or eradicate the development of germs inside the subject’s organisms. Moreover, it has been theorized that the peptide’s possible use as an antibiotic for research models might be translated into the capacity to prevent infection in some circumstances.